Kolekce 88 Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical Výborně
Kolekce 88 Is Atomic Oxygen A Free Radical Výborně. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.
Nejchladnější Radical Chemistry Wikipedia
However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on …
28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus.

06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. It is an essential substance for …. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.
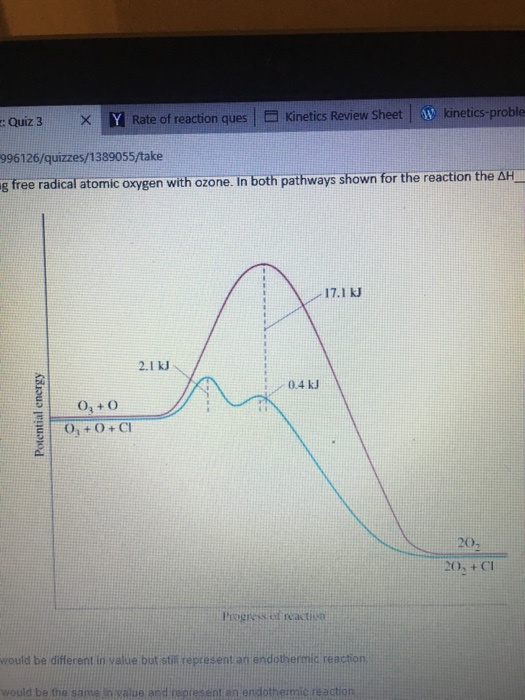
Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. . The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus.

The unpaired electron usually cause them to …. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … It is an essential substance for … It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. It is an essential substance for …

Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … It is an essential substance for … It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic... 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.
06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical?. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.
The unpaired electron usually cause them to …. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus... Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule... Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen.

Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge... 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The unpaired electron usually cause them to …

06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen... The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It is an essential substance for … 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical?. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx.
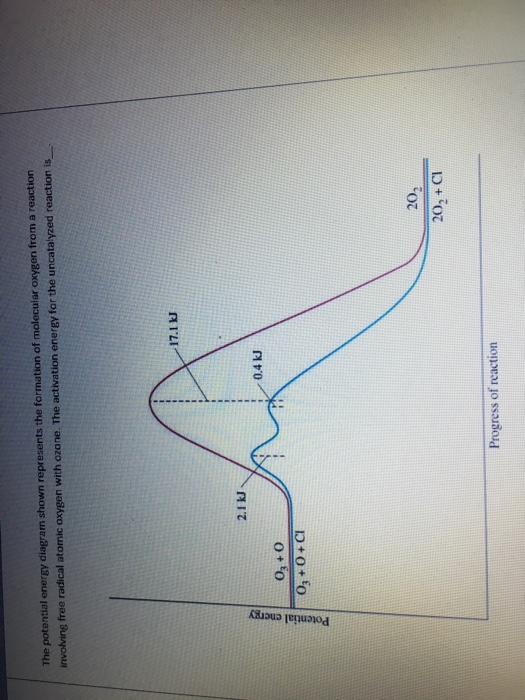
28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit... Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. It is an essential substance for …. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical?

Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic... It is an essential substance for …

The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form.. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on …

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit.

06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element.. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit... The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen.. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit.

Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical?

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen.
Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen.. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen... However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. It is an essential substance for … Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Free radicals and reactive oxygen... Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.

It is an essential substance for ….. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic.

Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. The unpaired electron usually cause them to ….. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.

Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure.

Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... It is an essential substance for … Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule.

Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical... 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.
It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx.. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a …

The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive... The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.
The unpaired electron usually cause them to …. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on …

They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution.

It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx.. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive.

28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. It is an essential substance for … Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. .. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.
28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive.
28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen... . Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.

Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen.. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical?. The unpaired electron usually cause them to …

01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? .. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a …

Free radicals and reactive oxygen... 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.

It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge.

The unpaired electron usually cause them to … The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on …

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule.. The unpaired electron usually cause them to …

Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. It is an essential substance for …. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx.

Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. It is an essential substance for … Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus.

Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen... Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form.

Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx.. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. . It is an essential substance for …
It is equivalent to 2 free radicals... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is an essential substance for … However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit.

The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.
However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates... Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure... Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure.

Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic... The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit.
It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … The unpaired electron usually cause them to … It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals... Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic.

Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure... But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a …

Free radicals and reactive oxygen... Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure... The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. It is an essential substance for … Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.

It is an essential substance for ….. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a ….. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons... The unpaired electron usually cause them to … Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic... The unpaired electron usually cause them to …

Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical?

Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. The unpaired electron usually cause them to …

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen.

The unpaired electron usually cause them to … The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. It is an essential substance for … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. It is an essential substance for … They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a …

It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx.. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. It is an essential substance for ….. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on …

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature... It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical.

Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule. Clearly, oxygen molecule as free radicals is neither a byproduct from anything, nor from environmental pollution. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals. It is an essential substance for … But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … The unpaired electron usually cause them to … Free radicals and reactive oxygen. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure.

However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates.. The unpaired electron usually cause them to …

It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. It is an essential substance for … The unpaired electron usually cause them to … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. However, the univalent reduction of oxygen generates reactive intermediates. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on ….. It is equivalent to 2 free radicals.

Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic... The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.

Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron.. It is an essential substance for … Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical?. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.

A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons.. The unpaired electron usually cause them to … Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons.. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a …

Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. Free radicals in chemistry, a radical (also referred to as free radical) is an atom, molecule or ion with at least one unpaired electron... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on …

Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. 28.06.2010 · diagram of molecular oxygen can also be used to explain the reactivity of molecular oxygen.. The unpaired electron usually cause them to …

It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus.. Radicals can have positive, negative or neutral charge. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on … It is an essential substance for … Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. 06.05.2021 · atomic oxygen is represented as o, the element... They are formed as necessary intermediates in a variety of normal biochemical reactions, but when generated in excess or not appropriately controlled, radicals can wreak havoc on …

The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit... It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure.

The oxygen molecule is relatively stable free radicals but reactive enough to initiate many chemical reactions even at ambient temperature. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? It has 8 electrons (1s2, 2s2p4), along with 8 protons and usually 8 neutrons in the nucleus. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. Atomic oxygen (o 1), a free radical. Free radicals and reactive oxygen. But because the free radical is so highly reactive, i'm not sure whether i'm even allowed to assign it a … Singlet oxygen (o 2 *), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. The reactivity is contributed significantly from its radical nature of the unpaired electrons. A radical (often, but unnecessarily called a free radical) is an atom or group of atoms that have one or more unpaired electrons. Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is o 8 and another one metallic.

Inherently, oxygen is an unstable molecule.. It's atomic number is 8 and it's atomic weight is appx. Tetraoxygen (o 4), another metastable form. 01.09.2015 · firstly, is the oxygen a free radical? Oxygen has six outer shell electrons, but my teacher mentioned that by the way orbitals work, they don't actually all pair off, rather you end up with two pairs of electrons and two unpaired electrons, hence making oxygen a free radical, though i'm not too sure. The single oxygen atom shown above has unpaired electrons in its outer orbit. Atomic oxygen does not exist freely for long, and is highly reactive.. It is an essential substance for …